Do You Know How Inductors Work?
Inductors, like resistors R and capacitors C, are an important part of passive components that are inevitably used in electronic devices. (Sitong Electronic has been established for 20 years and our engineers have 40 years of experience.)
Magnetic effect of electric current and coils
An electric current produces a magnetic field and has a magnetic effect on its surroundings. This is the "magnetic effect of electric current", which was discovered by Oster in 1820. It follows that parallel wires with currents flowing in the same direction attract each other, while parallel wires with currents flowing in the opposite direction repel each other. Moreover, Ampere also made a coil of wire into a cylindrical shape, called it solenoid. This is the originator of the solenoid coil used for antenna coils, etc. At that time, it was also discovered that solenoid coils with flowing currents exhibited the same properties as magnets.
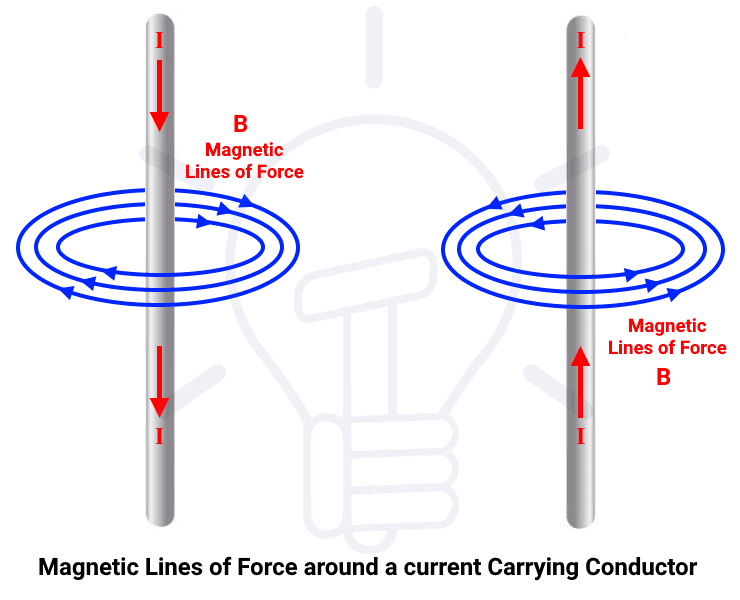
Electromagnetic induction and coil inductance
In contrast to the magnetic effect of current, which produces magnetic lines of force, the phenomenon of "electromagnetic induction", in which changes in magnetic flux produce electric potential, was discovered by Faraday in 1831.
The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is produced by a single coil. When the current flowing through a coil changes, the resulting magnetic flux also changes, creating an electric potential in the coil. This is called self-inductance. The electric potential (V) is expressed in the following equation, and the proportional constant L is called self-inductance. Usually the inductance of an inductor (coil) is this self-inductance.
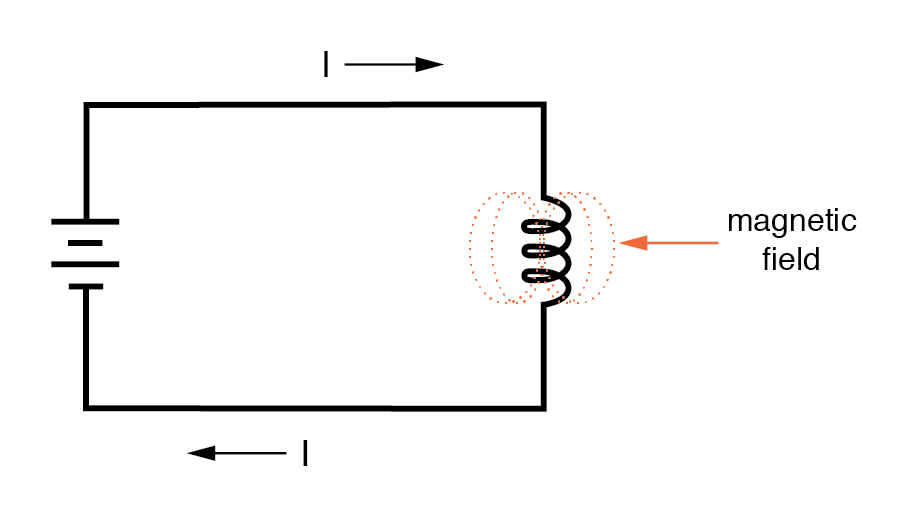
RF Cable Assembly: The Backbone of Seamless Communication
USB-C Cables: Empowering Connectivity and Efficiency
Understanding Wire Wound Resistors: A Comprehensive Guide
Demystifying Power Bank PCB Assembly: A Comprehensive Guide
The Versatile Eye Bolt: A Practical Solution for Various Applications
Unleashing the Power of TFT Display Modules
Why Choose Vertiv Liebert CRV Precision Air-Conditioned?
The principle of inductors
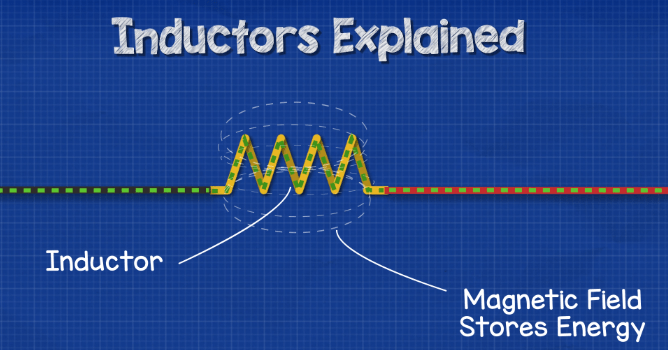
In a word, when an electric current passes through a wire, a magnetic field in the shape of concentric circles is generated around the wire. If the wire is bent into a "spring shape", the magnetic flux inside the inductor will point in the same direction, thus increasing the flux. By adjusting the number of turns, a magnetic field proportional to the number of turns can be generated. This is the principle of an inductor.
An electric current passing through an inductor will produce a magnetic field, and conversely, a change in magnetic field will produce an electric current.
Want to understand inductors better? Feel it in practice!
Sitong Electronic provides three types of inductors with free samples!
Do You Know How Inductors Work?
Guide of Isolation Transformer and Toroidal Transformer
Choosing the Right Power Battery for Electric Vehicles
What is the Difference Between SWA and Armoured Cable?
Understanding the Difference Between SWA and Armoured Cable
SWA Cable VS Armoured Cable
What Are the Advantages of Using an SMPS Transformer?
How to Use an Electric Blanket Switch Safely?
Advantages of Dry Type Power Transformers