How Does Induction Heating System for Forging Work?
I. Introduction
Induction heating in the forging industry is a revolutionary technology that has transformed traditional manufacturing processes. As a web content editor seeking to enhance reader engagement and drive website traffic, understanding the intricacies of how induction heating systems work for forging is crucial. In this article, we will explore the principles, components, and applications of induction heating, answering key questions to satisfy the readers' search intent.
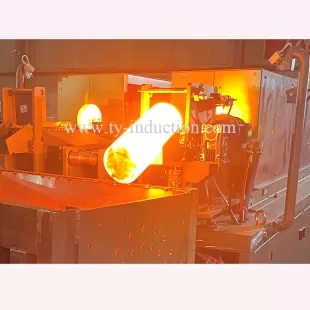
II. What is Induction Heating?
At its core, induction heating is a method of generating heat within a conductive material through the use of electromagnetic fields. In the context of forging, this process is instrumental in achieving precise and controlled temperatures for shaping metal.
III. Components of an Induction Heating System
The induction heating system comprises three main components: the power supply unit, induction coil, and workpiece. The power supply unit generates high-frequency alternating current, which passes through the induction coil, creating a powerful magnetic field. This magnetic field induces eddy currents within the workpiece, causing it to heat up.
IV. How Does Induction Heating Work in Forging?
In forging, the induction heating system is employed to heat metals to the desired temperature for shaping. The electromagnetic induction process ensures rapid and uniform heating, allowing for greater control over the forging process. As the metal reaches the required temperature, it becomes malleable, facilitating the forging of intricate shapes and designs.
V. Advantages of Induction Heating in Forging
The efficiency and precision of induction heating make it highly advantageous in forging applications. Unlike traditional heating methods, induction heating allows for quick and targeted temperature adjustments, reducing energy consumption and enhancing overall efficiency. This makes it a preferred choice for industries where precision and speed are paramount.
Related links:How Does a Sand Making Machine Work?
What is the Principle of Waste Air Separator?
What are the Advantages of Using Induction Heating for Forging?
What are the three basic types of hydraulic pumps?
What is the Height of a Container Ramp?
Different Types of Crushers
Revolutionizing Aluminum Cutting with Fiber Laser
VI. Applications of Induction Heating in Forging
Induction heating finds wide-ranging applications in the forging industry, particularly in the automotive, aerospace, and general manufacturing sectors. The ability to precisely control temperatures makes it suitable for various metalworking applications, from shaping components for automobiles to producing intricate parts for aerospace technologies.
VII. Common Misconceptions about Induction Heating
Addressing misconceptions is crucial to understanding the true benefits of induction heating. Some may believe it's a complex or costly process, but the reality is that technological advancements have made induction heating more accessible and cost-effective than ever before. Debunking these myths helps readers appreciate the advantages of adopting this technology.
VIII. Induction Heating vs. Traditional Heating Methods
Comparing induction heating to traditional methods highlights its superiority in forging applications. Unlike traditional furnaces or ovens, induction heating is faster, more energy-efficient, and allows for better temperature control. This section provides a detailed comparison, showcasing why industries are increasingly adopting induction heating.
IX. Key Considerations When Implementing Induction Heating
While the benefits of induction heating are evident, businesses considering its adoption must weigh certain factors. Initial investment costs, training requirements, and long-term benefits are crucial considerations. This section offers insights to help businesses make informed decisions when implementing induction heating systems.
X. Challenges and Solutions in Induction Heating for Forging
No technology is without its challenges. This section addresses common issues in induction heating, such as heat distribution and system maintenance, and explores innovative solutions that have been developed to overcome these challenges.
XI. Future Trends in Induction Heating for Forging
Looking ahead, the future of induction heating holds exciting possibilities. Emerging technologies, including advancements in materials and control systems, are poised to further enhance the efficiency and capabilities of induction heating in the forging industry.
XII. Conclusion
In conclusion, the induction heating system for forging is a cutting-edge technology that has reshaped the landscape of metalworking. Its efficiency, precision, and versatility make it a valuable asset for industries aiming to stay at the forefront of innovation. As businesses continue to embrace induction heating, the forging process is set to become even more streamlined and environmentally friendly.
Revolutionary Cigarette Pack Inspection Machine: Answers Your Top Queries on Efficiency, Quality, and Safety!
Revolutionizing PCB Inspection: Unveiling Cutting-Edge Technologies
Cable Cutting Made Effortless: Advanced Measuring Machine
Enhance Equipment Performance with Custom Hydraulic Cylinders: Uncovering the Benefits of Gear Rack Technology
When did the 6.7 Cummins come out?
Mastering ACF to PCB Soldering: Tips & Tricks
How much does it cost to set up a SMT line?